Three-phase asynchronous motor fault detection method - Database & Sql Blog Articles
2021-05-23
First, the motor can not start:
1, the motor does not turn and there is no sound: the power supply or winding has two or more phases open circuit, first check whether the power supply has voltage, if the three-phase voltage is balanced, then the fault is in the motor itself, the resistance of the three-phase winding of the motor can be detected, looking for The winding of the broken wire.
2, the motor does not turn but there is a buzzing sound: measuring the motor terminal, if the three-phase voltage is balanced and the rated voltage value, it can be judged to be a serious overload, the steps of the inspection: first remove the load, then the motor speed and sound is normal, It can be judged that the overload or the mechanical part of the load is faulty. If it does not rotate, you can turn the motor shaft with your hand. If it is tight or does not move, measure the three-phase current again. If the three-phase current is balanced, it is larger than the rated value. The mechanical part of the motor is stuck, it may be that the motor is short of oil, the bearing is rusted, or the damage is serious. The end cover or the oil cover is too oblique, and the rotor and the inner ring are touched (broom). When the motor shaft is turned by hand to some At a certain angle, I feel more strenuous or hear a periodic rub, which can be judged as a broom.
3, the motor speed is slow and there is a buzzing sound: this fault is expressed as the shaft vibrating east. If the measured phase current is zero, and the other two phase currents greatly exceed the rated current, it means that the two phases are running. The reason is: the circuit or The power supply is disconnected in one phase, or the motor winding is disconnected in one phase. A small-capacity motor can be used to directly measure whether it is on or off with a multimeter. Medium-capacity motors use multiple wires and are connected in parallel around multiple branches. It is more troublesome to check if several wires are broken or one parallel branch is disconnected. In this case, phase current balancing or resistance method is usually used. . The electric resistance method measures the resistance of the three-phase winding by a bridge, for example, the phase difference of the three-phase resistance is more than five, and the one phase with the larger resistance is the disconnected phase.
Experience has shown that most of the motor's open circuit faults occur at the ends of the windings, at the joints or at the lead wires.
Second, the fuse is blown or the thermal relay is disconnected when the motor starts.
1. Troubleshooting procedure: Check if the fuse is suitable, check if there is a short circuit in the circuit, check if the motor is shorted or grounded.
2, ground fault detection method: use the shake meter to detect the insulation resistance of the motor winding to the ground, when the insulation resistance is less than 0.2 megohms, the motor is seriously wet. Use the multimeter resistance file or the verification lamp to check step by step. If the resistance is small or the calibration lamp is dark, the winding is severely damp and needs to be dried. If the resistance is zero or the verification lamp is close to normal brightness, then the item is close. Ground. Winding grounding generally occurs in the motor outlet hole, the power cable inlet hole or the winding extension slot. For the latter case, if the grounding is not serious, insert the bamboo or insulating paper between the stator core and the winding. If it has not been grounded after inspection, it can be wrapped and coated with insulating varnish and then used.
3, the detection method of winding short-circuit fault: winding short-circuit condition has inter-turn short circuit, phase-to-phase short circuit. A Use a megger or multimeter to check the insulation resistance between any two phases. If it is found at 0.2 MΩ or zero, it means phase-to-phase short circuit. (When checking, all the wires of the motor lead should be taken apart.) B. Measure the current of the three-phase winding separately. The current is large. Short-circuit phase C. Short-circuit detector is used to check the short-circuit between the windings. D. The three-phase winding resistance is measured by the bridge. The resistance is small. The short circuit phase.
Third, the motor speed is lower than the rated speed after starting:
If several motors have such problems at the same time, the power supply grid voltage is usually too low.
If a motor starts to hum and has some vibration, check whether the stator winding is disconnected from one phase, and measure whether the three-phase current is balanced.
There is a click but no vibration to check if the three-phase voltage is too low.
When the air load is normal, the motor speed is normal, and the speed is reduced after loading.
Checking steps:
Firstly, the motor is started without load. If the speed is normal, the motor can be lightly loaded. If the speed is low, the mechanical part of the load is stuck. If the mechanical part is not faulty, the motor speed is not reduced, and the motor can be rated. Running within the range, if the motor speed drops, giving a feeling of not moving, it proves that the motor is faulty, the cause of this fault is: mistakenly connect the motor of the delta connection into a star, the squirrel cage rotor is broken If the motor is just wound, it may be that a certain pole phase is reversed.
Fourth, the motor vibration:
The motor is connected to the machine through the transmission mechanism. The vibration of the motor can cause mechanical vibration. The mechanical vibration will also vibrate the motor. The motor and the mechanical transmission part will be disconnected and then the motor will be started. If the vibration elimination is a mechanical failure, otherwise the motor will vibrate and vibrate. The reasons are: the motor base is not strong, the motor is not concentric with the shaft of the driven mechanical part, the rotor of the motor is unbalanced, the motor shaft is bent, the pulley shaft is eccentric, the squirrel cage is broken, the bearing is damaged, and the electromagnetic system is unbalanced. Motor broom.
5. There is noise when the motor is running:
The fault is divided into the mechanical part and the electromagnetic part of the motor. The method of distinguishing: first make the motor run energetically, listen carefully to the sound of the operation, and then stop the power, let the motor continue to run by inertia. If the abnormal sound disappears at this time, it means that the motor is electromagnetic. Failure, otherwise it is a mechanical failure of the motor.
Mechanical noise: The noise emitted by the A bearing may be that the bearing steel ball is damaged and the lubricating oil is too small. At this time, the head of a screwdriver is placed on the outside of the bearing oil cover, and the shank is attached to the ear, and the sound of the cymbal can be heard. B Air Mocha noise. This kind of sound is very uniform, not very strong, and can be judged to be normal. C Motor broom noise, this noise is characterized by a squeaky sound. For a motor that has just been repaired, if noise is found during operation, check whether the current is balanced, whether the rotation is flexible, and whether the speed reaches the rated speed. If there is no such problem, it may be that the insulating paper or bamboo chips in the stator slot protrudes beyond the slot, so that the sound of the rotor and the phase of the rotor are both pointed and high.
Electromagnetic noise: A rotor and stator length are not well matched. Rotor length refers to the distance from one bearing to another. The stator length refers to the distance from one bearing chamber to another. Under normal conditions, the stator length is slightly longer than the rotor length. One point, if there is too much difference, there may be a low "beep" sound. The B rotor is axially displaced, and this displacement may also generate electromagnetic noise, and the no-load current is increased, and the battery performance of the motor is lowered. C stator, the number of rotor slots is improperly matched, and another rotor is misplaced during assembly. The air between the stator and the stator is uneven, the stator rotor is out of round, and the shaft may be slightly bent.
In addition, motor winding phase loss, turn-to-turn short circuit, phase-to-phase short circuit, overload operation, etc. can cause electromagnetic noise.
Sixth, the motor temperature rise is too high or the winding is burned:
The number of positive and negative reversals is too trivial, so that the motor often works in the starting state, which often causes the temperature rise to be too high, and even burns the winding. Common reasons are: the mechanical card owner is driven, the ambient temperature is too high, the belt is too tight, the electromagnetic part is faulty, the power supply voltage is too high, too low, the gap between the motor end coils and the iron core vent is blocked. Fan blade damage, etc.
Seven, stator winding grounding:
1, the cause of the failure
A winding is damp, B motor insulation is aging (crack, crack, crisp, etc.) C. Magnetic material (iron filings, etc.) is dropped on the surface of the groove wall or coil. After a period of operation, drilling occurs at the magnetic material. The insulation is broken down and shorted. The D coil is loose or loosely tied in the groove, causing the insulation to wear and collide with the iron core to cause grounding. The E stator core rotates, causing the motor lead and the housing to be grounded or shorted.
2, inspection method:
A smoke method: For the grounding winding, put a lower voltage between the iron core and the coil, adjust the voltage with a voltage regulator, limit the current within 5 amps to prevent burning of the iron core, when the current passes through the grounding point, at the fault When heat is generated, the winding insulation can emit smoke or even sparks, causing a point of failure. B current orientation method: connect the first phase of the fault and the tail phase, and connect to the circuit under test. The current direction in the coil is as shown in the figure. The two currents flow to the grounding point together. A small magnetic needle is placed on the top of the slot, and the slot moves. The position where the magnetic needle changes direction is the slot where the grounding point is located, and then the small magnetic needle moves axially along the slot, and the small magnetic needle changes direction at the fault point, then this point is the grounding point.
Y series 3-phase cast iron housing induction motor
Y series motor is totally enclosed and fan cooled three phase squirrel cage induction motor. It is newly designed in conformity with the relevant rules of IEC&DIN42673 standards. The Y connection for motor of 3kw and below. And delta connection for 4kw and above.
Application:
Y series motors are widely used in places where there doesn't exist combustible, explosive or corrosive gas, and without any special requirements, such as machine tools, pumps, fans, transport machinery, mixer, agriculture machinery and food machines, etc.

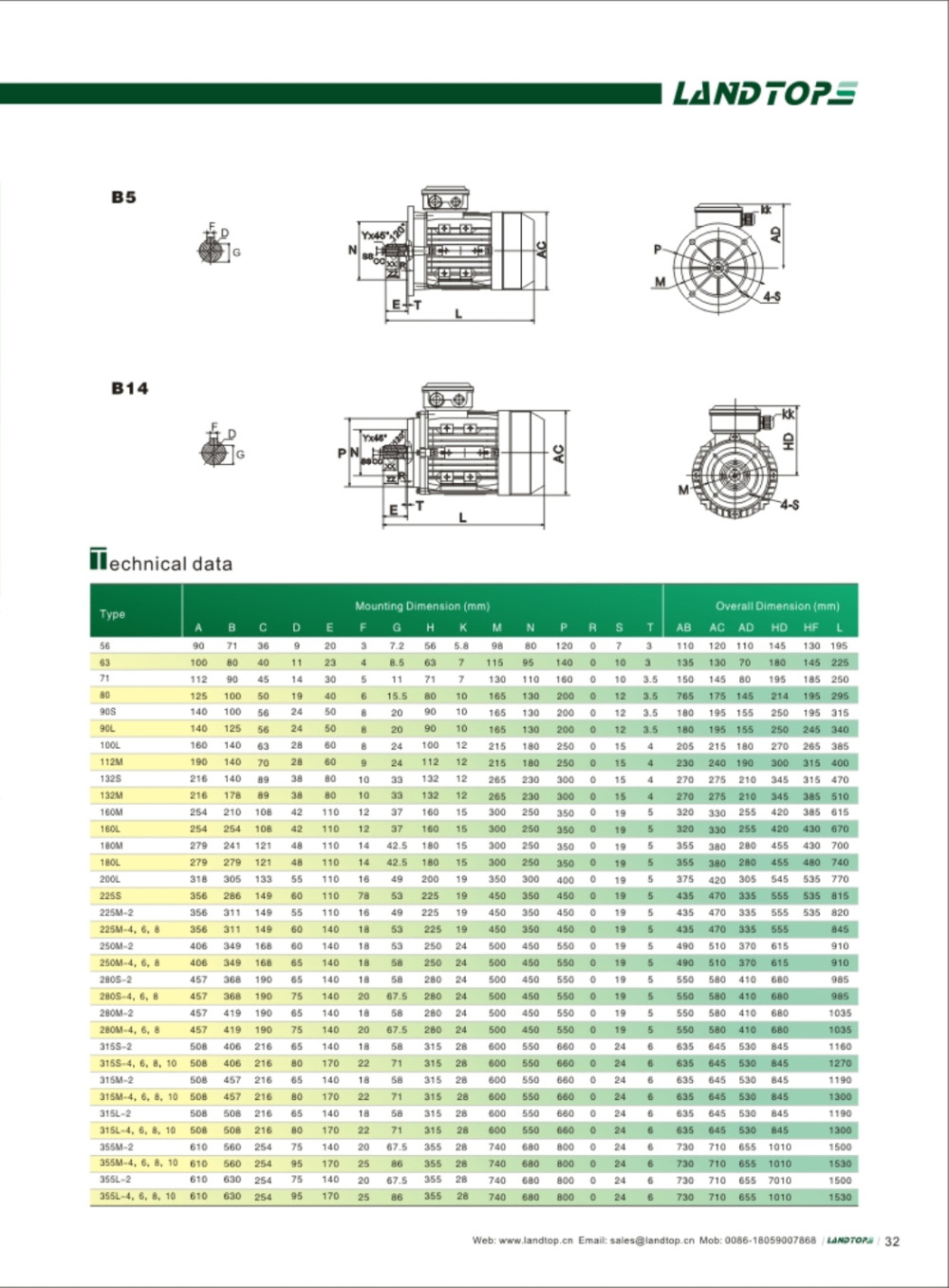
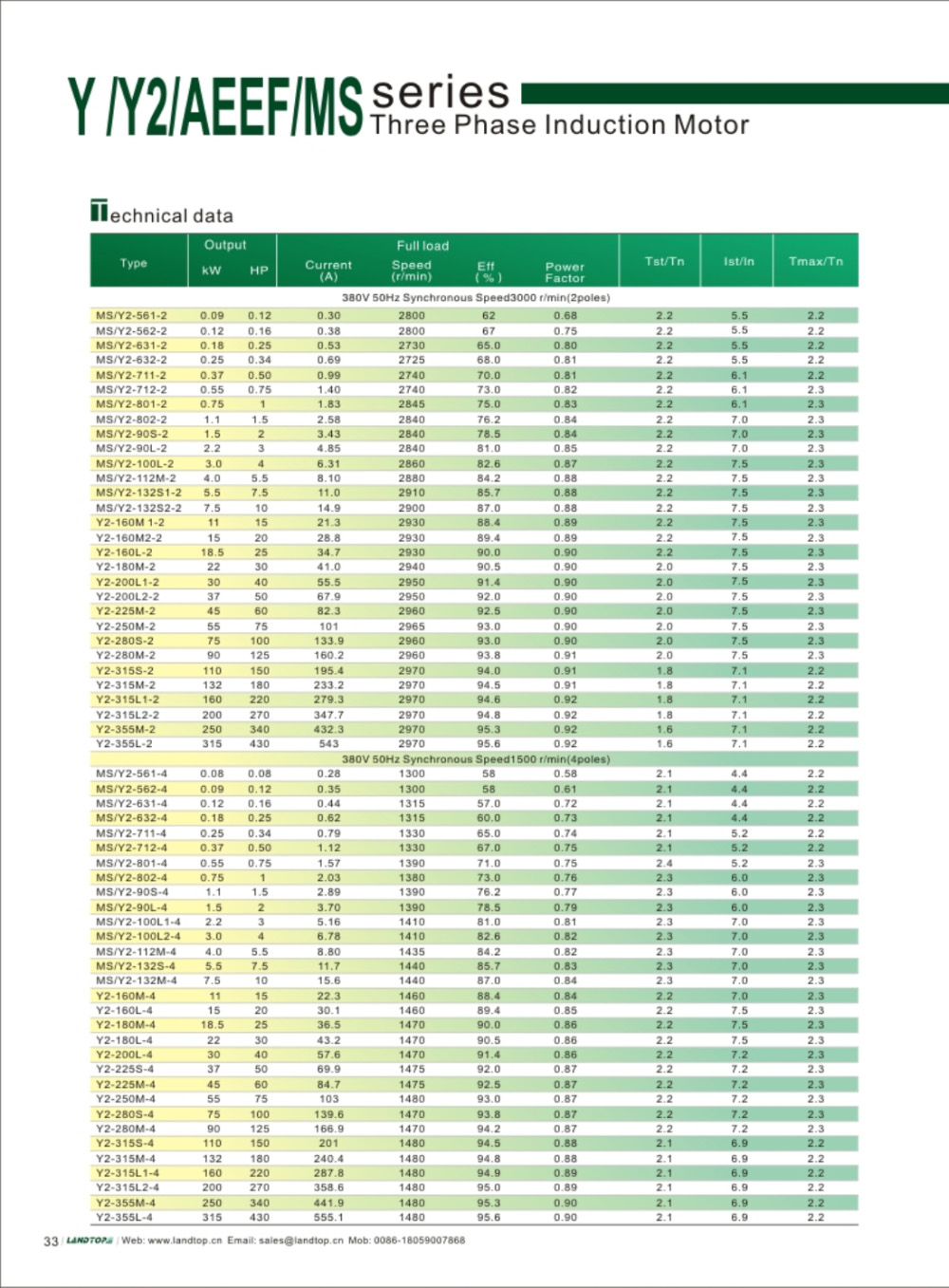
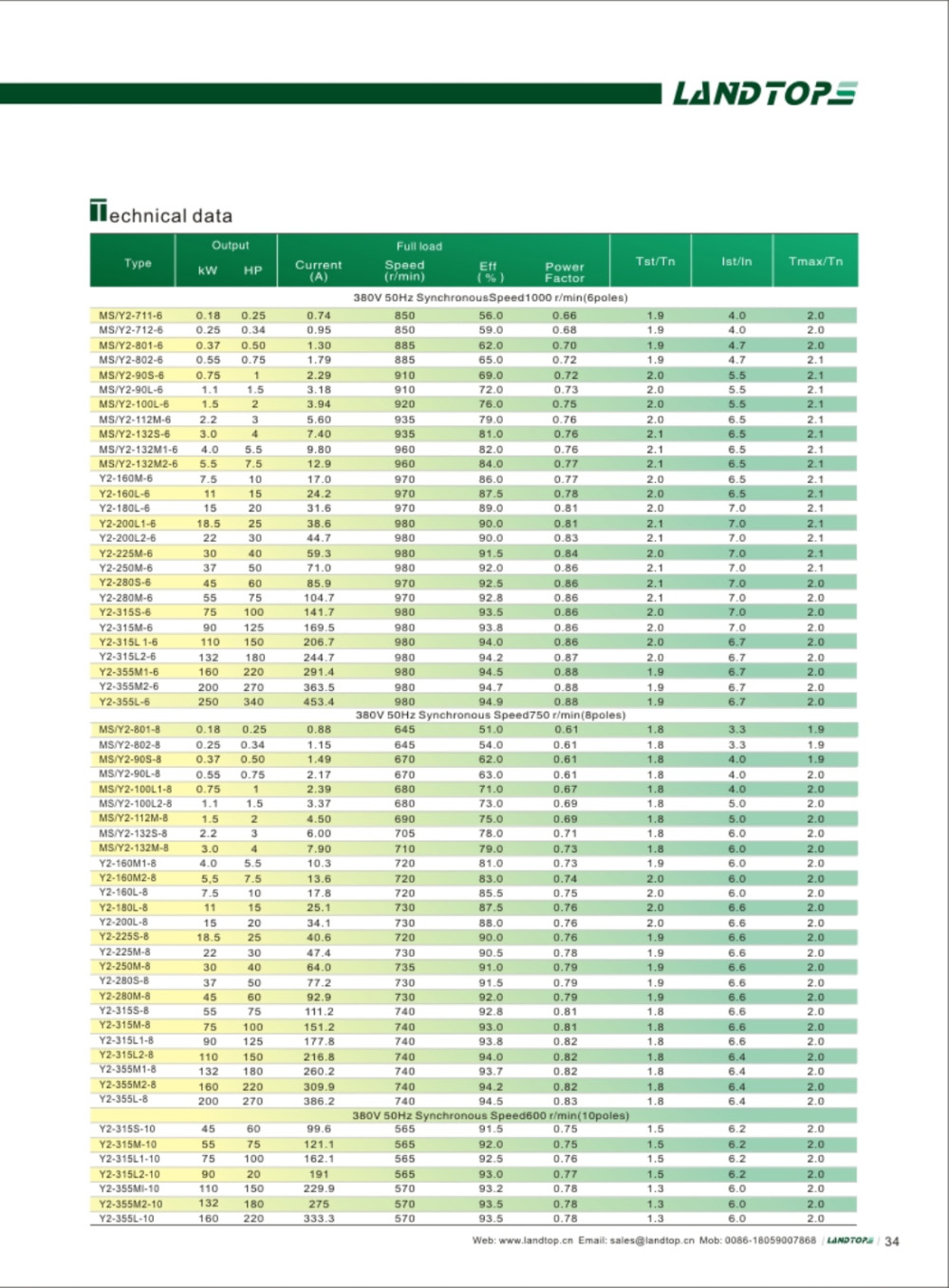
3 Phase Motor, Three Phase Motor, 3 Phase Induction Motor, Three Phase Electric Motor
Hengtong Generator Manufacture Co., Ltd http://www.landtopcos.com







